At Germanten Hospital, we often meet patients who are confused about their joint pain and bone health. Two terms, "osteoporosis" and "osteoarthritis" sound so similar that they are frequently used interchangeably. However, these are two very different medical conditions with unique causes, symptoms, and treatments. Understanding the distinction is the first and most crucial step toward getting the right care.
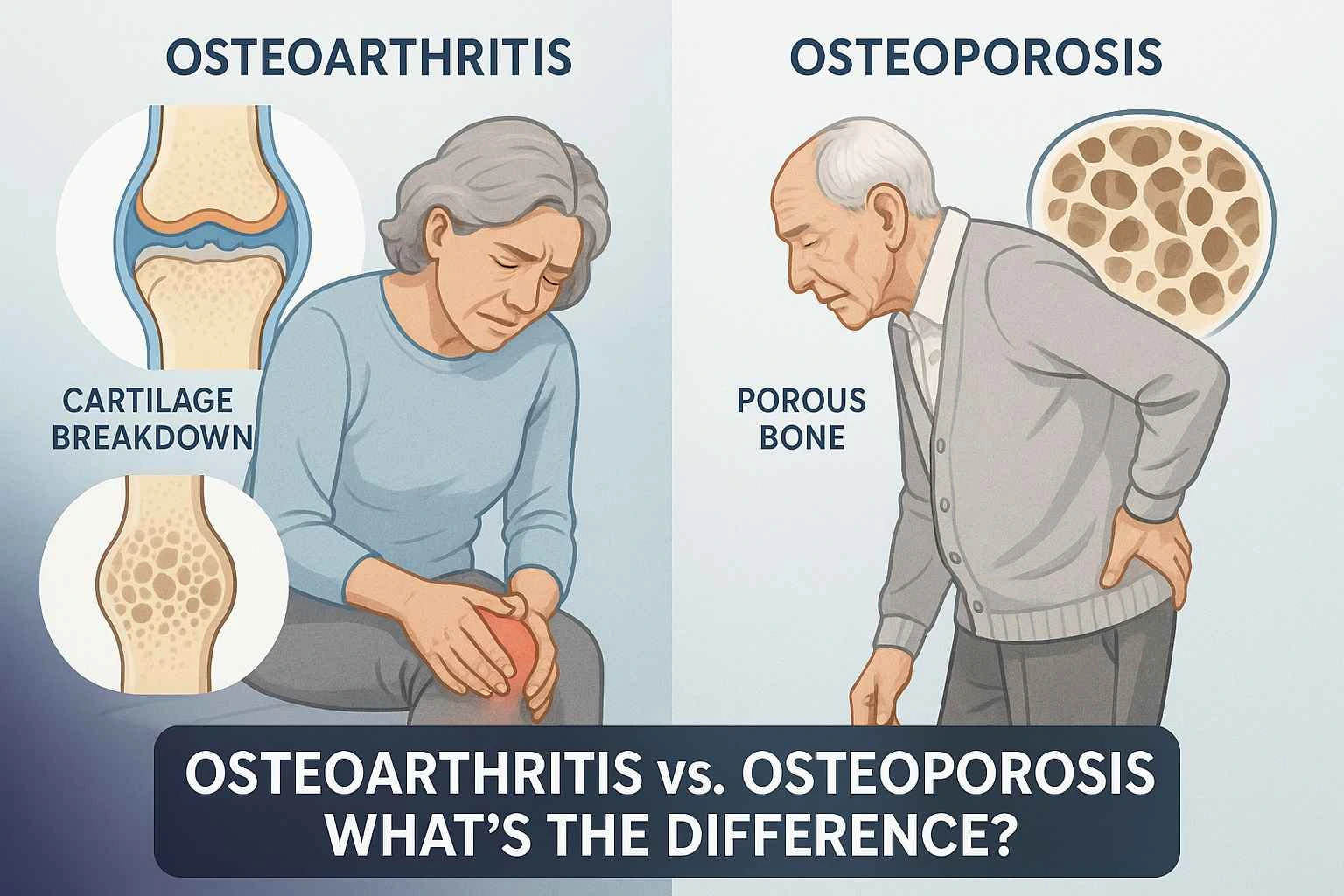
Definition: Osteoporosis is a "bone disease" where bones become weak and porous, risking fracture. Osteoarthritis is a "joint disease" where the protective cartilage wears down, causing pain and stiffness. One affects bone density, the other affects joint surfaces.
As one of the leading orthopedic hospitals in Hyderabad, our mission is to empower you with clear, accurate information. This comprehensive guide will break down everything you need to know about osteoporosis and osteoarthritis, helping you move from confusion to clarity and take control of your health.
Understanding Osteoarthritis: The "Wear and Tear" Disease
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most typical form of arthritis, affecting millions of people worldwide. Think of it as a problem of your joints—the complex mechanisms that allow you to bend, twist, and move.
What Exactly is Osteoarthritis?
Every joint in your body has a smooth, rubbery material called cartilage covering the ends of the bones. This cartilage acts like a shock absorber and a lubricant, allowing your bones to glide past each other without friction.
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition where this protective cartilage gradually wears down over time. As the cartilage thins, the joint space narrows, and eventually, the bones can start to rub directly against each other. This "bone-on-bone" contact is what causes the significant pain and stiffness associated with the disease. While it's often called a "wear and tear" disease, it affects the entire joint, causing changes in the bone and weakening the surrounding tissues.
Key Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
While OA can be painless in its early stages, symptoms develop and worsen as the cartilage degenerates. According to medical experts, you should watch for :
- Joint Pain: This is the hallmark symptom. The pain often worsens during or after movement and may improve with rest.
- Stiffness: You might feel particularly stiff when you wake up in the morning or after a long period of sitting or inactivity. This stiffness usually lasts for less than 30 minutes.
- Tenderness: The area around the affected joint may feel sore when you apply light pressure.
- Swelling: Soft tissue inflammation near the joint can cause noticeable swelling.
- Loss of Flexibility: You may find it difficult to move the joint through its complete range of motion.
- Grating Sensation: Some people feel a grating or scraping sensation, or hear popping and crackling sounds when they use the joint.
- Bone Spurs: These are extra bits of bone
that can form around the affected joint, feeling like hard lumps.
Which Joints Are Most Commonly Affected?
Osteoarthritis can sabotage any joint, but it most frequently occurs in :
- Knees: Pain when walking, climbing stairs, or getting up from a chair.
- Hips: Pain is often felt in the groin or inner thigh, not necessarily the outside of the hip.
- Hands: Affects the joints at the base of the thumb and the ones closest to the fingertips.
- Spine: Can cause pain and immobility in
the neck or lower back.
What Causes Osteoarthritis?
The risk of developing osteoarthritis increases with a combination of factors. Most experts agree that the primary risk factors include :
- Age: The risk naturally increases as you get older. A 2023 report from the Cleveland Clinic notes that over 80% of adults over 55 have some degree of OA.
- Joint Injury: A previous injury, even one from many years ago, can increase your risk.
- Obesity: Carrying extra body weight puts more pressure on weight-bearing joints like the hips and knees, accelerating cartilage wear.
- Genetics: A family history of OA can make you more susceptible.
- Repetitive Stress: Jobs or sports that place repeated strain on a particular joint can contribute to its development.
- Gender: Women are more probable to develop osteoarthritis, though the exact reasons are still being studied.
- Certain Metabolic Diseases: Conditions
like diabetes and high cholesterol are also related to a higher risk.
Understanding Osteoporosis: The "Silent Thief" of Bones
Now, let's shift our focus to osteoporosis. If osteoarthritis is a "joint problem," osteoporosis is
purely a "bone problem". It's a condition that weakens your bones from the inside out, often without
you even knowing it.
What Exactly is Osteoporosis?
The word "osteoporosis" literally means "porous bone". Your bones are living tissues that are in a constant state of renewal—old bone is broken down (a process called resorption) and replaced with new bone. Osteoporosis occurs when the composition of new bone doesn't keep up with the removal of old bone.
This imbalance causes the bones to lose density and mass, becoming weak, brittle, and porous. As a result, they can break much more easily. In severe cases, even a minor stress like bending over, lifting a grocery bag, or even a strong cough can cause a fracture.
Why You Won't Feel Osteoporosis Until It's Too Late
One of the most dangerous aspects of osteoporosis is that it is a "silent disease". Unlike osteoarthritis, which announces itself with pain and stiffness, osteoporosis typically has no symptoms in its early stages. Most people have no idea they have it until a bone breaks unexpectedly.
However, there are some subtle warning signs that may appear as the condition progresses :
- Loss of Height: Losing an inch or more in height over time can be a sign of compression fractures in your spine.
- Stooped Posture: As the vertebrae weaken and collapse, it can lead to a curving of the upper back, sometimes called a "dowager's hump."
- Back Pain: This can be caused by a fractured or collapsed vertebra.
- A Bone That Breaks Easily: A fracture
from a minor fall or bump that wouldn't normally cause such an injury is a major red
flag.
Which Bones Are Most at Risk?
While any bone can be impacted by osteoporosis, fractures most commonly occur in the :
- Hip
- Spine (vertebrae)
- Wrist
What Causes Osteoporosis?
The risk of osteoporosis is influenced by a mix of unchangeable and lifestyle-related factors. According to research from leading institutions like the Mayo Clinic, key risk factors include :
- Age: The risk increases greatly after the age of 50.
- Gender: Women are at much higher risk, especially after menopause when estrogen levels drop, as estrogen helps protect bone density.
- Family History: Having a parent or sibling with osteoporosis puts you at more prominent risk.
- Body Frame: Individuals with small, thin body frames are more susceptible as they may have less bone mass to begin with.
- Hormone Levels: Lower levels of estrogen in women or testosterone in men can weaken bones.
- Dietary Factors: A lifelong lack of calcium and vitamin D is a major contributor.
- Lifestyle Choices: A sedentary lifestyle, excessive alcohol consumption, and tobacco use all contribute to weaker bones.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions
like rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, kidney disease, and thyroid problems can increase
your risk.
Head-to-Head: Osteoporosis vs. Osteoarthritis at a Glance
To make the differences crystal clear, here's a simple comparison table that summarizes the key distinctions between these two conditions.
Getting the Right Diagnosis: The First Step to the Right Treatment
Because these conditions are so different, an accurate diagnosis is absolutely essential.
Self-diagnosing based on symptoms can be misleading and delay proper care. At Germanten, we use
state-of-the-art diagnostic tools to pinpoint the exact cause of your discomfort.
Why "It's Just Old Age" is a Dangerous Misdiagnosis
Many people dismiss the early signs of osteoarthritis—like morning stiffness or aching knees—as a normal part of getting older. This can be a critical mistake. While age is a risk factor, the pain and loss of function from OA are not something you simply have to "live with."
Diagnosing osteoarthritis typically involves :
- A Thorough Physical Examination: Our orthopedic specialists will talk to you about your symptoms, check your range of motion, and assess the affected joints for tenderness and swelling.
- Imaging Tests (X-rays): A simple X-ray is
highly effective for diagnosing OA. It allows us to see the physical changes in the joint,
such as the narrowing of the space between bones and the presence of bone spurs.
Diagnosing the "Silent Thief"
For osteoporosis, the diagnostic approach is different. Since it's a silent disease, we can't wait
for a fracture to happen. Proactive screening is key.
The gold standard for analyzing osteoporosis is a DEXA (or DXA) scan. This is a
quick, painless, and non-invasive type of X-ray that precisely measures your bone mineral density. A
regular X-ray cannot detect osteoporosis until you've already lost 30-50% of your bone mass, which
is far too late for effective prevention. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force advises routine
screening for all women aged 65 and older, and for younger women with increased risk
factors.
Finding the Best Orthopedic Treatment in Hyderabad: Your Options
Once we have an precise diagnosis, we can create a personalized treatment plan. The approaches for
osteoarthritis and osteoporosis are completely different, which is why the correct diagnosis is so
important.
Treatment Pathways for Osteoarthritis
The goal of OA treatment is to manage pain, reduce inflammation, and enhance your joint function so you can stay active.
- Lifestyle Modifications: For many, the first line of treatment includes weight management to reduce pressure on the joints and low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling to improve strength and flexibility.
- Physical Therapy: A structured physical therapy program can strengthen the muscles around the joint, providing better support and reducing pain.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like paracetamol and anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage symptoms. In some circumstances, cortisone injections directly into the joint can provide temporary relief.
- Advanced Surgical Solutions: When
conservative treatments are no longer effective and pain severely impacts your quality of
life, surgery may be the best option. At Germanten Hospital, we specialize in high-precision
joint replacement surgeries. Our expertise in Robotic
Knee Replacement and Total Hip
Replacement utilizes German precision technology to ensure optimal
implant placement and better long-term outcomes, solidifying our position as a provider of
the best orthopedic
treatment in Hyderabad.
Treatment Pathways for Osteoporosis
The objective of osteoporosis treatment is to slow or stop bone loss, increase bone density, and, most importantly, prevent fractures.
- Nutrition: A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is fundamental. We can advise on the right foods and supplements to ensure your body has the building blocks it needs for strong bones.
- Exercise: Weight-bearing exercises (like walking, jogging, and dancing) and strength training are crucial. These activities put gentle stress on your bones, which signals your body to make more bone mass.
- Medications: Several effective medications are available to treat osteoporosis. Bisphosphonates are the most common class of drugs that slow down the rate at which your body breaks down bone. Other options include hormone therapies and newer biologic drugs.
- Surgical Fracture Repair: If a fracture
does occur, our orthopedic surgeons are equipped to provide expert care. For painful spinal
compression fractures, a minimally invasive procedure
called Kyphoplasty can be conducted to stabilize the bone and relieve
pain. For hip fractures, surgical repair is almost always necessary.
The Final Takeaway: Don't Guess, Get Assessed
While both Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis are common as we age, they are not the same.
- Osteoarthritis is a mechanical "wear and tear" problem in your joints that causes pain.
- Osteoporosis is a silent problem of low
density in your bones that leads
to fractures.
The most important thing you can do is not to ignore your symptoms or dismiss them as just "getting
older." Persistent joint pain, a loss of height, or a bone that breaks too easily are all signs that
you need a professional medical evaluation.
At Germanten Hospital, we
combine world-class diagnostic capabilities with a comprehensive range of treatment options—from
physical therapy and medication management to advanced robotic surgery. If you are looking for one
of the premier orthopedic hospitals in
Hyderabad, your search ends here.
Ready to take the next step? Don't live with pain or uncertainty. Schedule a consultation with our expert orthopedic doctors today and get a clear diagnosis and personalized care you deserve.